

The Canon EOS 77D for microscope and macroscope imaging

Canon’s EOS 77D DSLR camera was released in April 2017 as the successor to the EOS 750D. We tested the EOS 77D on several microscopes from different manufacturers using our modularly designed LM digital adapter solutions. In this article, we are sharing the results of our tests, and we will also cover the different connection options available.
Attaching the camera to the photo tube of a Zeiss Primo Star was an easy task with our new DD2XZPrimo adapter solution.

A different type of adapter (DSLRCTCW_Pro) is needed for Nikon microscopes with V-T photo tube (42 mm internal diameter) and C-mount photo tube (factor 1x).

Thanks to its largely polycarbonate exterior, the EOS 77D weighs only about 500 grams and thus can be attached to the microscope’s eyepiece tube without any danger of damage. Trying to attach heavy cameras to the eyepiece tube of a lightweight microscope would require additional support for the camera. We attached the EOS 77D to an eyepiece tube with an internal diameter of 30 mm, using the DSLRCT + TUST30W adapter combination.


With our focusable wide-field adapter, an image field enlarged by 25% can be obtained. The order code for this adapter if used on a 30 mm eyepiece tube is DSLRCTW.
In addition to these standard connection options, we also offer adapter solutions for special microscopes, such as split lamps or surgical microscopes. Adapter solutions for conventional, commercially available microscopes are generally in stock for immediate availability.
The EOS 77D has a highly sensitive APS-C sensor (22.5 mm x 15 mm) with 24 megapixels. Compared to most “true” microscope cameras with tiny sensors (0.5–6.4 mm x 4.8 mm), it is significantly more powerful and thus yields considerably better image quality at a particularly favourable price. The camera’s mechanical, focal plane shutter can shoot at speeds of up to 1/4,000 second. This makes it possible to capture fast processes or moving objects without blurring. Shutterless cameras (such as C-mount or industrial cameras) on the other hand, tend to have more image noise in the image than their shuttered counterparts, because light hits the sensor before an exposure is fully ended. Thanks to Canon’s mature sensor technology, the EOS 77D is also well suited for fluorescence imaging applications.
It has a colour image sensor with an integrated Bayer (RGB) filter system and is thus also a great choice for imaging techniques that take advantage of colour information.
The camera’s image processor is able to capture up to 6 frames per second. Images can be stored in JPEG and RAW format. The EOS 77D features Bluetooth, WiFi and NFC connectivity and has an HDMI mini OUT terminal. Movies can be shot at Full HD.
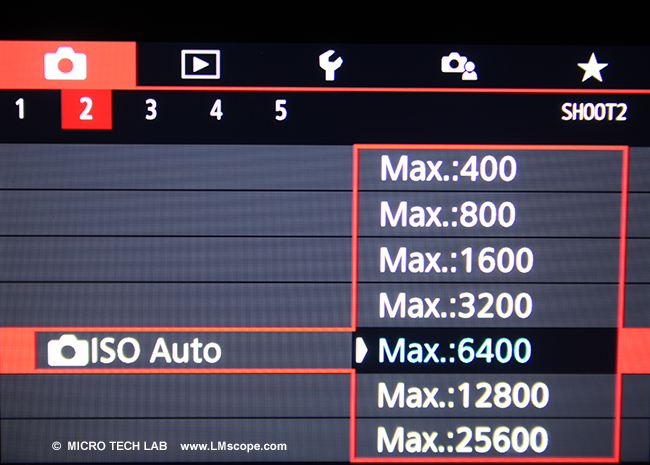
The EOS 77D supports a variety of microscopy techniques: transmitted light, incident light, dark field, phase contrast, differential interference contrast and even fluorescence imaging. With a native ISO range of 100 to 25,600, the camera is also well suited for low-illumination techniques such as fluorescence microscopy.
The display is an important aspect when it comes to installing a camera on a microscope for image acquisition, and the EOS 77D does not disappoint in that respect: it features a TFT LCD touchscreen panel with a display diagonal of 7.7 cm (3.0’’). The screen can be pulled out from the body by 180 degrees and rotated through 270 degrees, which is a great advantage over fixed screens in terms of efficiency and ergonomic characteristics. Also, the EOS 77D adds a small LCD info display at the top.
For routine use in the laboratory, we recommend replacing the battery with an externally powered battery dummy. This way, the camera can be used continuously without stopping to charge it.
The Canon EOS 77D supports all basic functions that are essential for photomicrography, such as manual ISO adjustment or disabling auto power-off. The ability to deactivate auto shut-off is a major benefit for presentations and projects that require the camera to be running over an extended period of time.
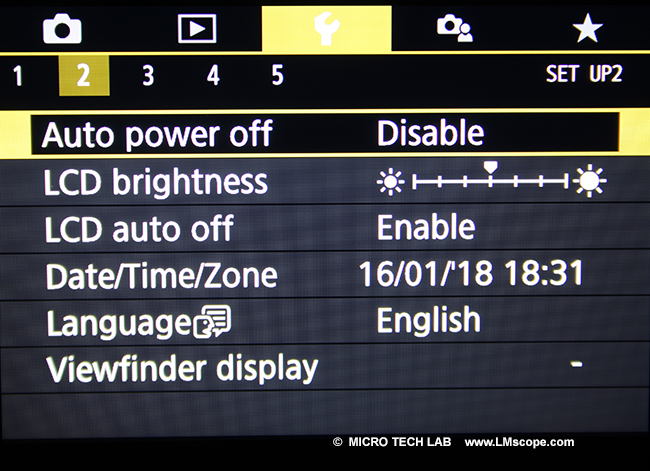
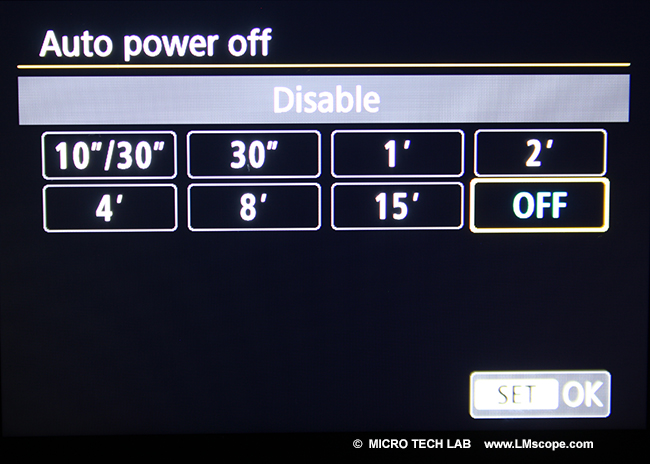
Unfortunately, the EOS 77D is missing the in-camera HDR mode, where images at different exposure settings are merged into one frame to increase the dynamic range captured. For users who need that particular feature, we recommend the Canon EOS 80D.
In a laboratory setting, the EOS 77D can be controlled remotely from a PC/Mac using the proven Canon Utility software, which is included for free with the camera.
Alternatively, remote control from a smartphone or tablet is possible with Canon’s Camera Connect app. A brief description of how the software and app performed on a similar camera is included in our Canon EOS 200D test report.
Conclusion: The Canon EOS 77D is a good mid-range camera that costs around EUR 500 (body only). It is more powerful than many C-mount microscope cameras and can be used for a variety of microscope imaging techniques. For users who need an integrated HDR mode for scientific documentation, the slightly higher priced Canon EOS 80D would be the better choice.
New LM Digital Adapter for: Canon EOS R3 / Canon EOS R6 Mark II / Canon EOS R8 / Canon EOS R5 II / Canon EOS R5 / Canon EOS R6 / Canon EOS R / Canon EOS Ra (Astro) / Canon EOS RP / Canon EOS R7 / Canon EOS R10 / Canon EOS 1D X Mark III / Canon EOS 1D X Mark II / Canon EOS R100 / Canon EOS 1D X / Canon EOS 90D / Canon EOS 5D Mark IV / Canon EOS 6D Mark II / Canon EOS M6 Mark II / Canon EOS 250D / Canon EOS 850D / Rebel T8i / Canon EOS 6D / Canon EOS M200 / Canon EOS 5DS R ( without low-pass filter) / Canon EOS 80D / Canon EOS M50 Mark II / Canon EOS 5DS / Canon EOS M50 / Canon EOS 70D / Canon EOS 200D / Canon EOS 800D / Rebel T7i / Canon EOS 77D / Canon EOS 5D Mark III / Canon EOS 60D / Canon EOS 750D / Rebel T6i / Canon EOS 760D / Rebel T6s / Canon EOS 5D Mark II / Canon EOS 1D Mark IV / Canon EOS 7D Mark II / Canon EOS 600D / Rebel T3i / Canon EOS 650D / Rebel T4i / Canon EOS 700D / Rebel T5i / Canon EOS 2000D / Rebel T7 / Canon EOS 7D / Canon EOS 550D / Rebel T2i / Kiss X4 Digital / Canon EOS 1300D / EOS Rebel T6 / Canon EOS 4000D / Canon EOS 100D / Canon EOS 50D / Canon EOS 1200D / EOS Rebel T5 / EOS Kiss X70 / Canon EOS 1100D / Rebel T3 /
